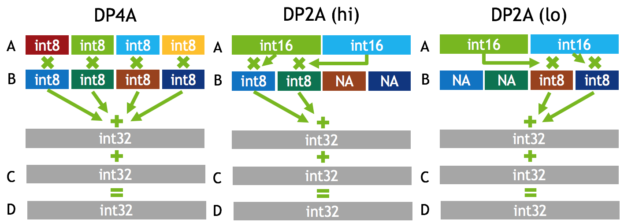
// 1. 初始化掩码和累加器
// mask = _mm256_set1_epi8(0x03); 用于提取2-bit数据。
// accu = _mm256_setzero_si256(); 用于累加结果。
// 2. 分组处理
// 外层循环:每次处理32组。
// 内层循环:遍历每组中的32个元素。
// 对每一组数据,分别取出2-bit并与8-bit数据做乘法累加(点积)。
// 3. 数据解码
// 2-bit数据拆成4个bit组(shift和mask操作)。
// 8-bit直接载入。
// 使用 _mm256_maddubs_epi16 指令做乘法累加。
// 4. 累加所有结果
// 使用 _mm256_add_epi16 和 _mm256_add_epi32 指令合并结果。
// 最后用 hsum_i32_8 对 SIMD 累加结果求和,得到最终点积。
*s = (float)sumi;,将结果赋值给输出指针。
#include <vector>
#include <type_traits>
// #include "ggml-bitnet.h"
// #include "ggml-quants.h"
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#define QK_I2_S 128
#define QK_I2 128
#include <immintrin.h>
#include <cstdint>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
// horizontally add 8 int32_t
static inline int hsum_i32_8(const __m256i a) {
const __m128i sum128 = _mm_add_epi32(_mm256_castsi256_si128(a), _mm256_extractf128_si256(a, 1));
const __m128i hi64 = _mm_unpackhi_epi64(sum128, sum128);
const __m128i sum64 = _mm_add_epi32(hi64, sum128);
const __m128i hi32 = _mm_shuffle_epi32(sum64, _MM_SHUFFLE(2, 3, 0, 1));
return _mm_cvtsi128_si32(_mm_add_epi32(sum64, hi32));
}
void print_m256i(__m256i vec) {
uint8_t bytes[32];
_mm256_storeu_si256((__m256i*)bytes, vec);
for (int i = 0; i < 32; ++i) {
printf("%02x ", bytes[i]);
if ((i + 1) % 16 == 0) printf("\n");
}
}
// x 指向 2-bit 量化数据,y 指向 8-bit 数据。
// 数据被分成多个组,便于后面的 SIMD 并行处理。
// 主要变量:
// QK_I2_S 通常为 128,表示每组的元素数。
// nb = n / QK_I2_S,组数。
// group32_num = nb / 32,每 32 组为一大组。
// la_num = nb % 32,剩余组数。
void ggml_vec_dot_i2_i8_s(int n, float * s, size_t bs, const void * vx, size_t bx, const void * vy, size_t by, int nrc) {
const uint8_t * x = (uint8_t *)vx;
const int8_t * y = (int8_t *)vy;
const int nb = n / QK_I2_S;
const int group32_num = nb / 32;
const int la_num = nb % 32;
const int groupla_num = nb % 32 != 0 ? 1 : 0;
// n : 128 nb : 1 group32_num : 0 la_num : 1 groupla_num : 1
std::cout << "n : " << n
<< " nb : " << nb
<< " group32_num : " << group32_num
<< " la_num : " << la_num
<< " groupla_num : " << groupla_num
<< std::endl;
__m256i mask = _mm256_set1_epi8(0x03);
__m256i accu = _mm256_setzero_si256();
for (int i=0; i < group32_num; i++){
std::cout << "i : " << i << std::endl;
__m256i accu32 = _mm256_setzero_si256();
for (int j=0; j < 32; j++) {
// 128 index
__m256i xq8_3 = _mm256_loadu_si256((const __m256i*)(x + i * 32 * 32 + j * 32));
__m256i xq8_2 = _mm256_srli_epi16(xq8_3, 2);
__m256i xq8_1 = _mm256_srli_epi16(xq8_3, 4);
__m256i xq8_0 = _mm256_srli_epi16(xq8_3, 6);
// each 32 index
xq8_3 = _mm256_and_si256(xq8_3, mask);
xq8_2 = _mm256_and_si256(xq8_2, mask);
xq8_1 = _mm256_and_si256(xq8_1, mask);
xq8_0 = _mm256_and_si256(xq8_0, mask);
// each 32 index
__m256i yq8_0 = _mm256_loadu_si256((const __m256i*)(y + i * 128 * 32 + j * 128 + 0));
__m256i yq8_1 = _mm256_loadu_si256((const __m256i*)(y + i * 128 * 32 + j * 128 + 32));
__m256i yq8_2 = _mm256_loadu_si256((const __m256i*)(y + i * 128 * 32 + j * 128 + 64));
__m256i yq8_3 = _mm256_loadu_si256((const __m256i*)(y + i * 128 * 32 + j * 128 + 96));
// 128 index accumulation add
// split into 32 accumulation block
// each block each 128 index accumulated 4index
// each index maximum 256
// each block maximum 4 * 256
// each block accumulation maximum 127 * 256
// each 32 group index (128 index in one group) needs cast to int32
xq8_0 = _mm256_maddubs_epi16(xq8_0, yq8_0);
xq8_1 = _mm256_maddubs_epi16(xq8_1, yq8_1);
xq8_2 = _mm256_maddubs_epi16(xq8_2, yq8_2);
xq8_3 = _mm256_maddubs_epi16(xq8_3, yq8_3);
accu32 = _mm256_add_epi16(accu32, _mm256_add_epi16(xq8_0, xq8_1));
accu32 = _mm256_add_epi16(accu32, _mm256_add_epi16(xq8_2, xq8_3));
}
accu = _mm256_add_epi32(_mm256_madd_epi16(accu32, _mm256_set1_epi16(1)), accu);
}
for (int i = 0; i < groupla_num; i++){
__m256i accula = _mm256_setzero_si256();
for (int j = 0; j < la_num; j++) {
// 128 index
// 例子中的128个int2,分成4组,每组32个int2
// 128个int2
// xx1 xx2 xx3 xx4 xx5 xx6 xx7 xx8 (int 16)
// 00 xx1 xx2 xx3 xx4 xx5 xx6 xx7 (shift right 2bit)
// 00 00 xx1 xx2 xx3 xx4 xx5 xx6 (shift right 4bit)
// 00 00 00 xx1 xx2 xx3 xx4 xx5 (shift right 6bit)
__m256i xq8_3 = _mm256_loadu_si256((const __m256i*)(x + group32_num * 32 * 32 + j * 32));
__m256i xq8_2 = _mm256_srli_epi16(xq8_3, 2);
__m256i xq8_1 = _mm256_srli_epi16(xq8_3, 4);
__m256i xq8_0 = _mm256_srli_epi16(xq8_3, 6);
// each 32 index
// mask: 00000011 00000011
// -- -- -- xx4 -- -- -- xx8 (int 16)
// 00 -- -- xx3 -- -- -- xx7 (shift right 2bit)
// 00 00 -- xx2 -- -- -- xx6 (shift right 4bit)
// 00 00 00 xx1 -- -- -- xx5 (shift right 6bit)
// int2通过移动bit位置和mask,拆分成了int8表示,就可以直接和int8进行运算了
xq8_3 = _mm256_and_si256(xq8_3, mask);
xq8_2 = _mm256_and_si256(xq8_2, mask);
xq8_1 = _mm256_and_si256(xq8_1, mask);
xq8_0 = _mm256_and_si256(xq8_0, mask);
print_m256i(xq8_3);
printf("-----\n");
print_m256i(xq8_2);
printf("-----\n");
print_m256i(xq8_1);
printf("-----\n");
print_m256i(xq8_0);
printf("-----\n");
// x中的int2每间隔4个数字为一组
// 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03
// 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03 03
// -----
// 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02
// 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02 02
// -----
// 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01
// 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01
// -----
// 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
// 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
// each 32 index
// 例子中的128个int8数据,分成4组,每组32个int8数据
// xx1 xx2
__m256i yq8_0 = _mm256_loadu_si256((const __m256i*)(y + group32_num * 128 * 32 + j * 128 + 0));
__m256i yq8_1 = _mm256_loadu_si256((const __m256i*)(y + group32_num * 128 * 32 + j * 128 + 32));
__m256i yq8_2 = _mm256_loadu_si256((const __m256i*)(y + group32_num * 128 * 32 + j * 128 + 64));
__m256i yq8_3 = _mm256_loadu_si256((const __m256i*)(y + group32_num * 128 * 32 + j * 128 + 96));
print_m256i(yq8_0);
printf("-----\n");
print_m256i(yq8_1);
printf("-----\n");
print_m256i(yq8_2);
printf("-----\n");
print_m256i(yq8_3);
// 按顺序存储,相邻的32个int8为一组
// -----
// 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f
// 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f
// -----
// 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e 2f
// 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 3a 3b 3c 3d 3e 3f
// -----
// 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 4a 4b 4c 4d 4e 4f
// 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 5a 5b 5c 5d 5e 5f
// -----
// 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 6a 6b 6c 6d 6e 6f
// 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 7a 7b 7c 7d 7e 7f
// 128 index accumulation add
// split into 32 accumulation block
// each block each 128 index accumulated 4index
// each index maximum 256
// each block maximum 4 * 256
// each block accumulation maximum 127 * 256
// each 32 group index (128 index in one group) needs cast to int32
// 乘加运算
// xx1, xx5 (16bit)
// yy1, yy2 (16bit)
// res = xx1 * yy1 + xx5 * yy2
xq8_0 = _mm256_maddubs_epi16(xq8_0, yq8_0);
xq8_1 = _mm256_maddubs_epi16(xq8_1, yq8_1);
xq8_2 = _mm256_maddubs_epi16(xq8_2, yq8_2);
xq8_3 = _mm256_maddubs_epi16(xq8_3, yq8_3);
// printf("-----\n");
// print_m256i(xq8_3);
// printf("-----\n");
// print_m256i(xq8_2);
// printf("-----\n");、
// 打印第1组乘加计算结果
print_m256i(xq8_1);
printf("-----\n");
// print_m256i(xq8_0);
// printf("-----\n");
// 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01
// 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01 01
// 乘加计算
// 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e 2f
// 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 3a 3b 3c 3d 3e 3f
// 结果
// 41 00 45 00 49 00 4d 00 51 00 55 00 59 00 5d 00
// 61 00 65 00 69 00 6d 00 71 00 75 00 79 00 7d 00
accula = _mm256_add_epi16(accula, _mm256_add_epi16(xq8_0, xq8_1));
accula = _mm256_add_epi16(accula, _mm256_add_epi16(xq8_2, xq8_3));
}
accu = _mm256_add_epi32(accu, _mm256_madd_epi16(accula, _mm256_set1_epi16(1)));
}
int sumi = hsum_i32_8(accu);
*s = (float)sumi;
}