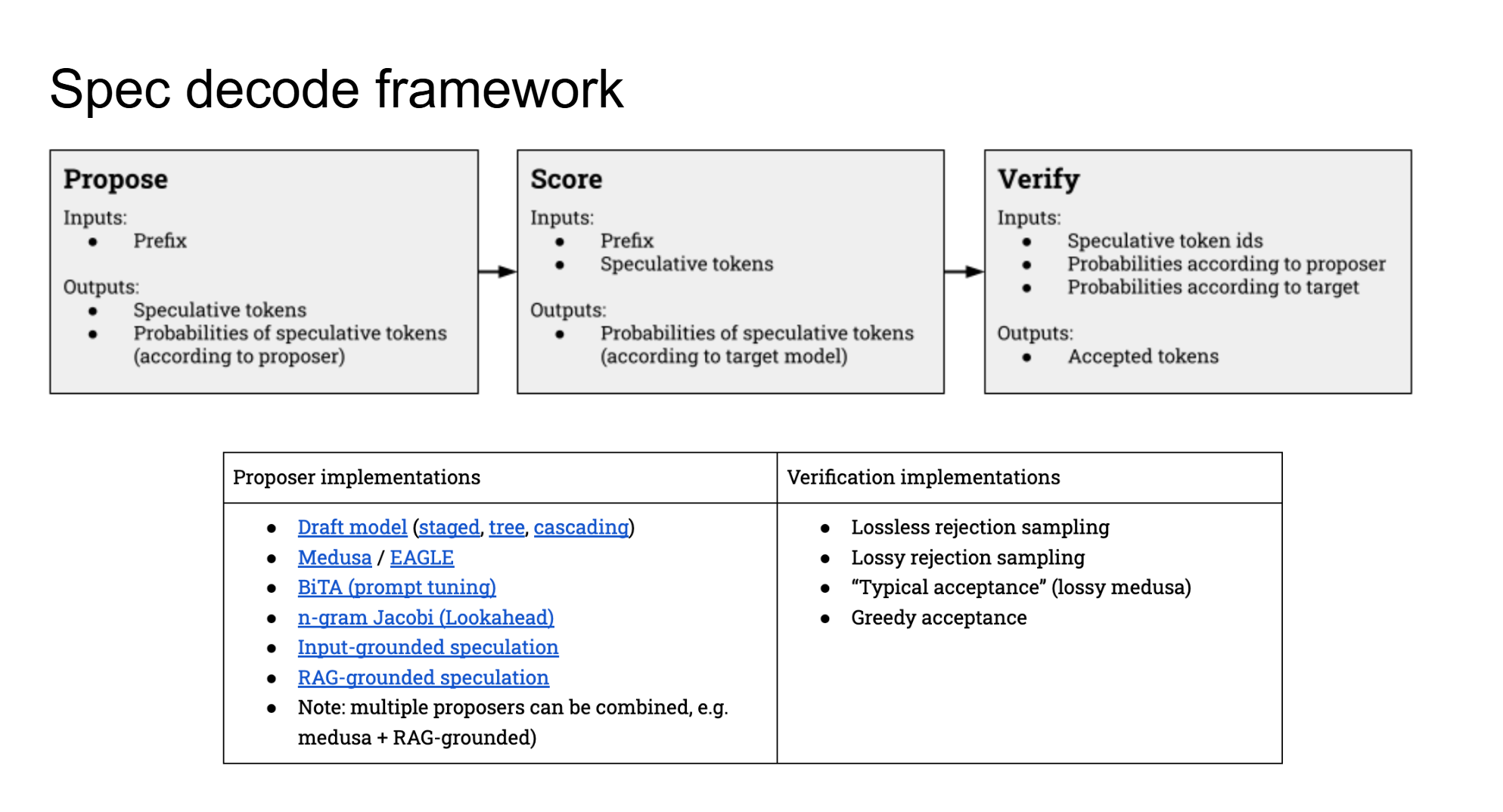
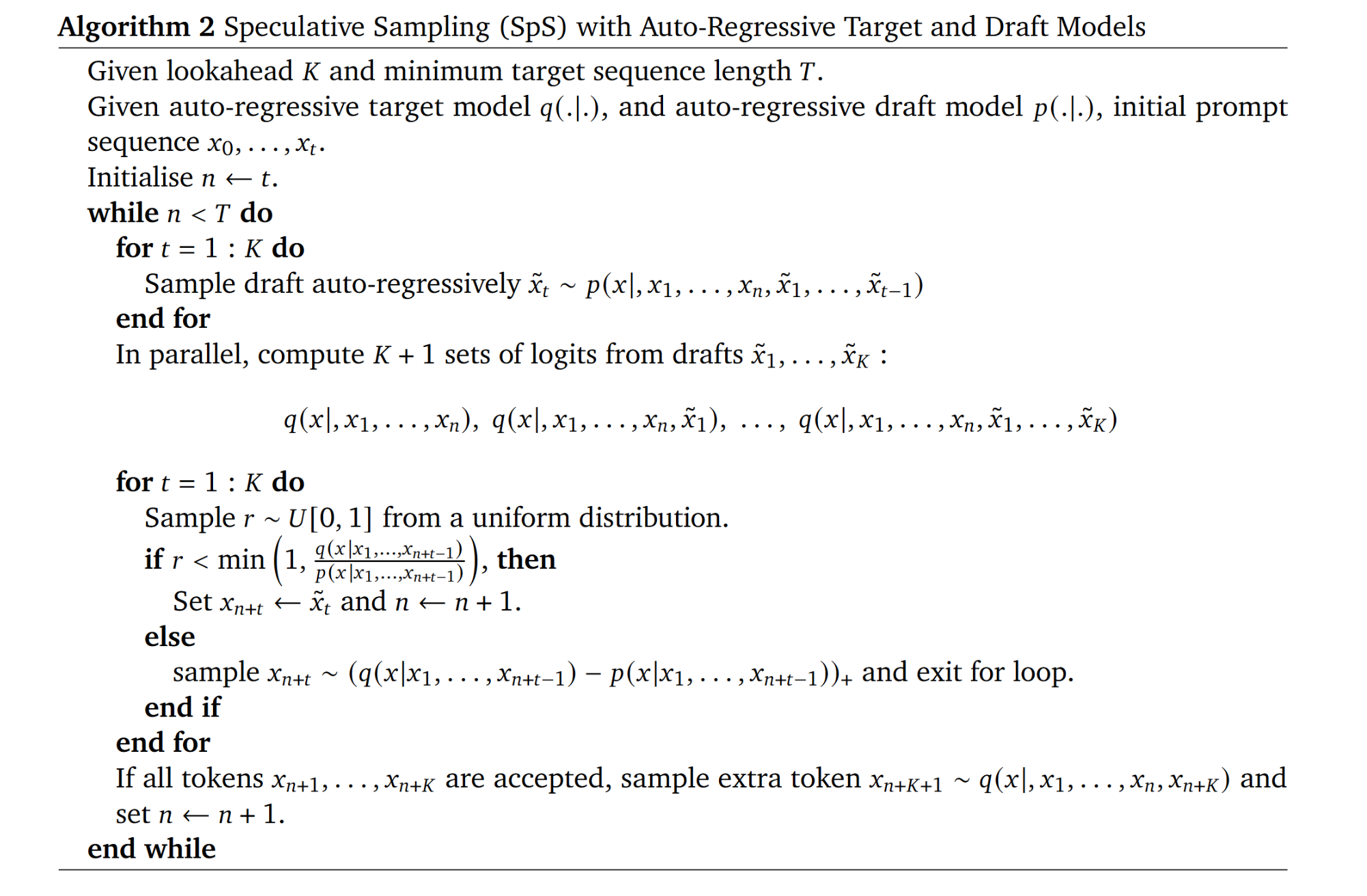
def _get_accepted(
self,
target_probs: torch.Tensor, # [batch_size, k, vocab_size]
draft_probs: torch.Tensor, # [batch_size, k, vocab_size]
draft_token_ids: torch.Tensor, # [batch_size, k]
) -> torch.Tensor:
r"""Create bool matrix over the proposed draft tokens. If
True, then a token can be accepted, else it should be
rejected.
Given :math:`q(\hat{x}_{n+1}|x_1, \dots, x_n)`, the probability of
:math:`\hat{x}_{n+1}` given context :math:`x_1, \dots, x_n` according
to the target model, and :math:`p(\hat{x}_{n+1}|x_1, \dots, x_n)`, the
same conditional probability according to the draft model, the token
is accepted with probability:
.. math::
\min\left(1, \frac{q(\hat{x}_{n+1}|x_1, \dots, x_n)}
{p(\hat{x}_{n+1}|x_1, \dots, x_n)}\right)
This implementation does not apply causality. When using the output,
if a token is rejected, subsequent tokens should not be used.
Returns a bool tensor of shape [batch_size, k] specifying which tokens
are accepted.
"""
batch_size, k, _ = draft_probs.shape
batch_indices = torch.arange(batch_size,
device=target_probs.device)[:, None]
probs_indicies = torch.arange(k, device=target_probs.device)
# shape [batch_size, k]
selected_draft_probs = draft_probs[batch_indices, probs_indicies,
draft_token_ids]
# shape [batch_size, k]
selected_target_probs = target_probs[batch_indices, probs_indicies,
draft_token_ids]
uniform_rand = torch.rand(batch_size,
k,
dtype=self.probs_dtype,
device=target_probs.device)
capped_ratio = torch.minimum(
selected_target_probs / selected_draft_probs,
torch.full((1, ), 1, device=target_probs.device))
# 对应论文中算法公式,如果概率比小于比值,则接受该 draft token
accepted = uniform_rand < capped_ratio
return accepted